Jarvis Island
|
Background:
 |
First discovered by the British in 1821, the uninhabited island was annexed by the US in 1858, but abandoned in 1879 after tons of guano had been removed. The UK annexed the island in 1889, but never carried out plans for further exploitation. The US occupied and reclaimed the island in 1935. Abandoned after World War II, the island is currently a National Wildlife Refuge administered by the US Department of the Interior; a day beacon is situated near the middle of the west coast. |
| Geography | Jarvis Island |
|
Location:
|
Oceania, island in the South Pacific Ocean, about half way between Hawaii and the Cook Islands |
|
Geographic coordinates: | 0 22 S, 160 03 W |
|
Map references:
|
Oceania |
|
Area:
|
total: 4.5 sq km
water: 0 sq km land: 4.5 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
about eight times the size of The Mall in Washington, DC |
|
Land boundaries:
|
0 km |
|
Coastline:
|
8 km |
|
Maritime claims - as described in UNCLOS 1982 (see Notes and Definitions):
|
territorial sea: 12 NM
exclusive economic zone: 200 NM |
|
Climate:
|
tropical; scant rainfall, constant wind, burning sun |
|
Terrain:
|
sandy, coral island surrounded by a narrow fringing reef |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: unnamed location 7 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
guano (deposits worked until late 1800s), terrestrial and aquatic wildlife |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 0%
permanent crops: 0% other: 100% (1998 est.) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
0 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
the narrow fringing reef surrounding the island poses a maritime hazard |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
no natural fresh water resources |
|
Geography - note:
|
sparse bunch grass, prostrate vines, and low-growing shrubs; primarily a nesting, roosting, and foraging habitat for seabirds, shorebirds, and marine wildlife |
| People | Jarvis Island |
|
Population:
|
uninhabited
note: Millersville settlement on western side of island occasionally used as a weather station from 1935 until World War II, when it was abandoned; reoccupied in 1957 during the International Geophysical Year by scientists who left in 1958; public entry is by special-use permit from US Fish and Wildlife Service only and generally restricted to scientists and educators; visited annually by US Fish and Wildlife Service (July 2004 est.) |
| Government | Jarvis Island |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Jarvis Island |
|
Dependency status:
|
unincorporated territory of the US; administered from Washington, DC, by the Fish and Wildlife Service of the US Department of the Interior as part of the National Wildlife Refuge system |
|
Legal system:
|
the laws of the US, where applicable, apply |
|
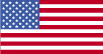
Flag description:
|
the flag of the US is used |
| Economy | Jarvis Island |
|
Economy - overview:
|
no economic activity |
| Transportation | Jarvis Island |
|
Waterways:
|
none |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
none; offshore anchorage only; note - there is one small boat landing area in the middle of the west coast and another near the southwest corner of the island |
|
Transportation - note:
|
there is a day beacon near the middle of the west coast |
| Military | Jarvis Island |
|
Military - note:
|
defense is the responsibility of the US; visited annually by the US Coast Guard |
| Transnational Issues | Jarvis Island |
|
Disputes - international:
|
none |


 Home
Home