| Earth from Space is a free eBook describing our planet from a satellite's perspective. Fore more information, please read the About pages. |

|

Home  Asia Asia  North Korea North Korea  Baitoushan Volcano Baitoushan Volcano |
|






|
|
Baitoushan VolcanoPosition of center of photo (Lat/Long): [42.00397/128.05138] |
|
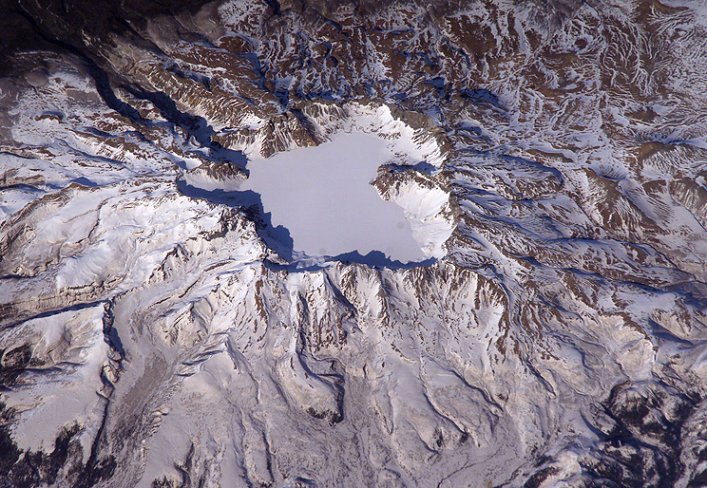 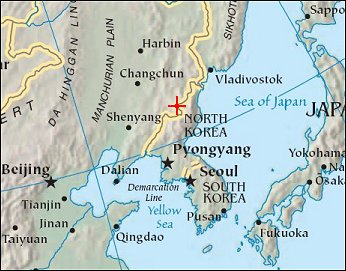 One of the largest known eruptions of the modern geologic period (the Holocene) occurred at Baitoushan Volcano (also known as Changbaishan in China and P'aektu-san in Korea) about 1000 A.D., with erupted material deposited as far away as northern Japan - a distance of approximately 1,200 kilometers. The eruption also created the 4.5-kilometer-diameter, 850-meter-deep summit caldera of the volcano, which is now filled with the waters of Lake Tianchi (or Sky Lake). This oblique astronaut photograph was taken during the winter season, and snow highlights frozen Lake Tianchi and lava flow lobes along the southern face of the volcano. One of the largest known eruptions of the modern geologic period (the Holocene) occurred at Baitoushan Volcano (also known as Changbaishan in China and P'aektu-san in Korea) about 1000 A.D., with erupted material deposited as far away as northern Japan - a distance of approximately 1,200 kilometers. The eruption also created the 4.5-kilometer-diameter, 850-meter-deep summit caldera of the volcano, which is now filled with the waters of Lake Tianchi (or Sky Lake). This oblique astronaut photograph was taken during the winter season, and snow highlights frozen Lake Tianchi and lava flow lobes along the southern face of the volcano.
Baitoushan last erupted in 1702, and geologists consider it to be dormant. Gas emissions were reported from the summit and nearby hot springs in 1994, but no evidence of renewed activity of the volcano was observed. The Chinese-Korean border runs directly through the center of the summit caldera, and the mountain is considered sacred by the predominantly Korean population living near the volcano. Lake Tianchi is a popular resort destination, both for its natural beauty and alleged sightings of unidentified creatures living in its depths (similar to the legendary Loch Ness Monster in Scotland). |
| Source of material: NASA |
Further information: WikiPedia article on Baitoushan Volcano
Last Update: 2011-03-30

